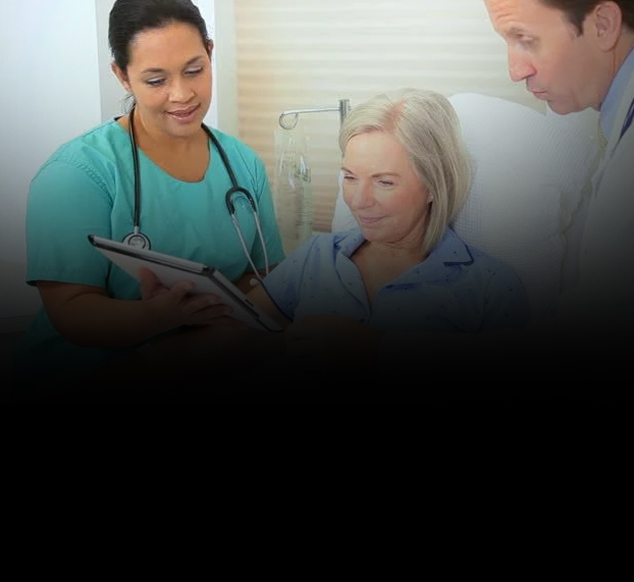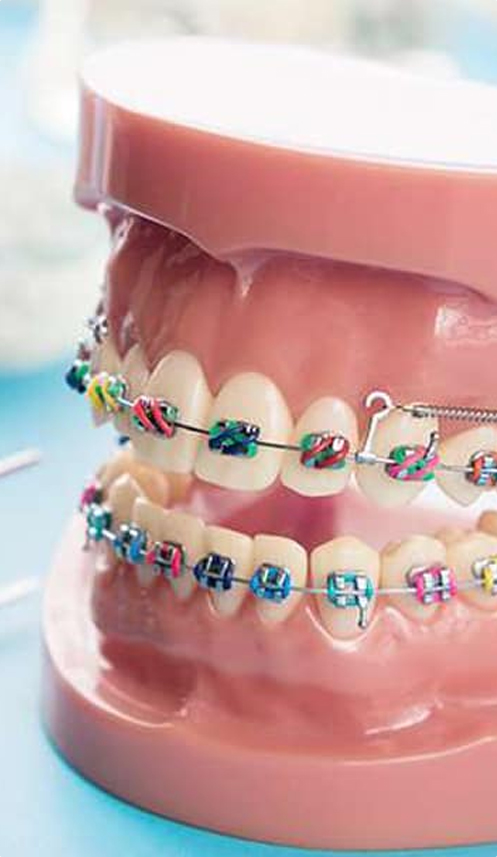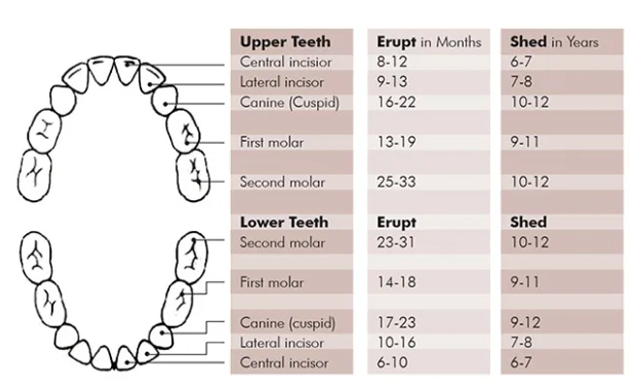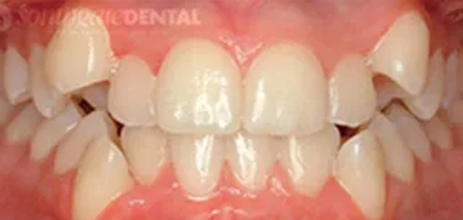
If the patient has narrow jaws, in most cases there is not be enough space for all the teeth. The orthodontist may have to remove teeth to make room for the others during the course of treatment.
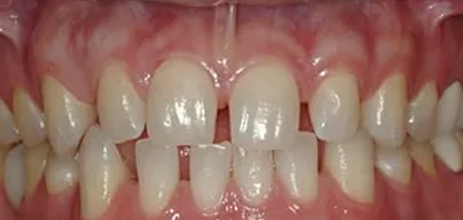
If there are spaces/gaps between the teeth, because a tooth is missing, or the teeth have simply not filled up the mouth. The orthodontist will close the spaces during treatment, but there may also be a need for Implant or Prosthetic (crown/bridge) work after the Orthodontic treatment is completed.
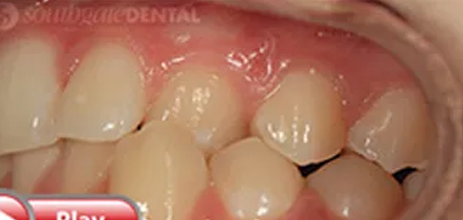
Is when there is an abnormal relation of one or more teeth on one arch/jaw to the opposing tooth or teeth of the other arch/jaw. This is usually caused by a deviation of tooth position or abnormal jaw position. This type of bite can be treated with a combination of ortho treatment and the use of intra oral elastics, but in severe cases the patient may require surgery.
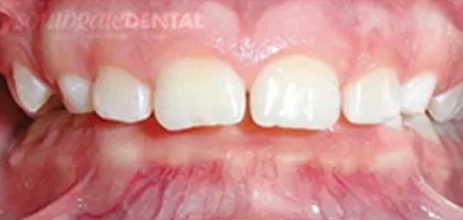
Is when the teeth are clenched, the upper ones come down over the lower ones too much. In some cases the lower teeth will bite the gum/palate on the upper arch/jaw when the teeth are closed together and this can lead to the loss of the front teeth.
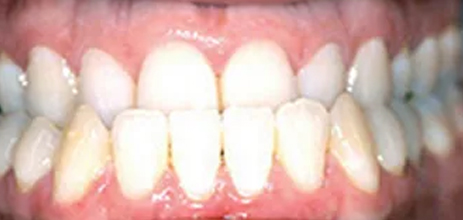
Is when the upper teeth are too far back, or the lower teeth bite too far forward. The earlier this is treated the better the chances are to avoid requiring surgery later. The optimal time to treat this is approximately 7/8 years of age while the child is still growing. The orthodontist will use a removable appliance to help to train the jaws in a better position. The patient may still have to wear fixed orthodontic appliances (train tracks) afterwards. In some cases (mainly adults) this treatment will involve surgery.
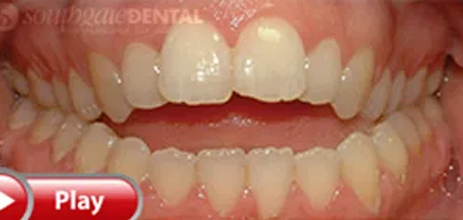
Is when the teeth are clenched, there is an opening between the upper and lower teeth. A lot of children experience anterior (front teeth) open bites between losing their baby teeth and gaining their adult teeth, which can last 1 to 2 years. Some of the major causes of an open bite are from thumb or finger sucking, pacifier use, lip and tongue habits, inadequate nasal airway creating the need for an oral airway; enlarged tonsils and adenoids, and skeletal growth abnormalities.